Phylum Mollusca
Including over 50 000 living species & 35 000 fossil species.
They are without cuticle soft bodies animals.
Characteristic features of Phylum Mollusca
Living Molluscs are highly specialised for a different mode of life.
 |
| Hypothetical Molluscs |
Body plan
Bilateral symmetrical
Triploblastic
They are soft-bodied & unsegmented
Their body is divided into 3 regions,
they are,
1.Head
2.Foot
3.Visceral mass
A fleshly fold called the mantel. It covers the visceral mass.
The chamber created by the mantel between the head & the body called mantel cavity.
Head
The head is lying anterior to the foot.
The head contains mouth & oral structures.
It bears 2 pair of tentacles and one pair of eyes borne on a stalk.
Foot
The foot is large & highly muscular organ.
It's formed by flattening of the ventral surface of the body.
It acts as hydrostatic properties of the blood system.
Foot largely secretes mucous & slime.
This muscular foot is modified for creeping slowly on a substratum.
Some of them burrowing & swimming using their muscular foot.
Visceral mass
It's formed a sort of a dome on the dorsal surface of the body.
Its dark colour and it contains internal organs like the digestive system, reproductive system,
excretory system.
Mantal
Thin, transparent & soft covering
Locate at the beneath of the shell.
Mantel cavity/Pillial cavity
This cavity serves as exit site for the excretory, reproductive, digestive systems.
The gills of aquatic molluscs lie within this cavity.
Posterior part of the mantel cavity includes anus, excretory pores, ctenidia.
Shell
Secreted by the mantel & calcium carbonate.
It serves as a protective device of the body.
It has different patterns of the shell.
It's consists of 3 layers,
1.Periostracum layer.
2.Prismatic layer.
3.Nacreous layer.
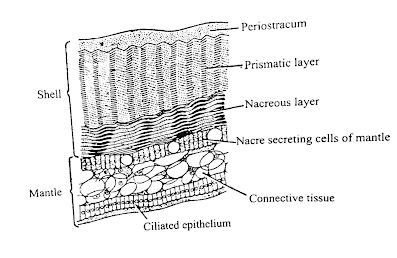 |
| Structure of the shell and the mantel |
1.Periostracum layer.
This is the outermost layer.
Formed by chitin like compound.
Thin & transperant layer.
Secreted by the edge of the mantel.
This layer responsible for the colour of the shell.
2.Prismatic layer.
Thick layer in the middle of the shell.
It's secreted by the mantel edge.
It consists of crystals of Calcium carbonate.
It gives strength & hardness to the shell.
3.Nacreous layer.
The innermost layer of the shell.
It's secreted by the outer surface of the mantel.
It's consists of calcium carbonate and conchiolin.
Internal system and other characters
Digestive system
Complete digestive system.
In herbivorous have a very long digestive system, carnivorous have a shorter digestive system.
The buccal cavity contains a special feeding structure called "Radula".
Radula
This used to feed.
Some herbivorous forms used to the tongue or rasping organ.
Some are used to drill holes through the shell of prey.
The radula is a ribbon-like plate covered with numerous chitinous teeth.
The old teeth are lost at the anterior end(due to constant use) and new teeth are formed at the posterior end.
Radula lies in the Radula sac, that locates at the floor of the buccal cavity.
The radula sac rest on a cartilaginous structure called Odonotophore.
The animal pulls the radula backwards & forwards like tongue by special muscle attached to the odontophore.
 |
| Radula in the mouth |
Respiratory system
They include the gill, known as ctenidium.
The ctenidium is the organ of respiratory in aquatic molluscs.
These are elongated and highly vascular, feather-like structures in mantel cavity.
The terrestrial molluscs respiration by lungs.
This is no true lungs. But the highly vascularized inner wall of the mantel.
Some molluscs gas exchange by the mantel.
Circulatory system
Open circulatory system.
Dorsally placed heart it surrounded by coelomic cavity called Pericardial cavity.
Their blood is blue in colour because of copper-based respiratory pigment haemocyanin in the plasma.
Excretory system
One to six pairs of sac-like nephridia or kidneys.
(waste material drained into the pericardial coelom, by ultrafiltration.
pass nephridial tubes and finally, empty into the mantel cavity.)
The excretory fluid contains Ammonia, urea, uric acid.
Nervous system
 |
| Nervous system with ganglions |
Sense organs
They have,
Tentacles.
Pair of eyes.
Pair of statocysts.
Osphradia.
 |
| eye |
 |
| Oshphradium |
 |
| Statocyst |
Statocysts found in the foot, they act as equilibrium.
Reproduction and Development
Molluscs are dioceous. sexes are separate.
The gonads and ducts are usually single.
Fertilization in internal or external.
cleavage is a spiral.
Their first larval stage is Trochophore larvae.
Trochophore larvae are converted into veliger larva(unique to molluscs).
Trochophore larvae & veliger larva both are free-swimming.
 |
| Veliger larva |




0 Comments
Post a Comment